Travel Demand Concentration in Metro Systems May Decrease Efficiency
Published on Mon Oct 23 2023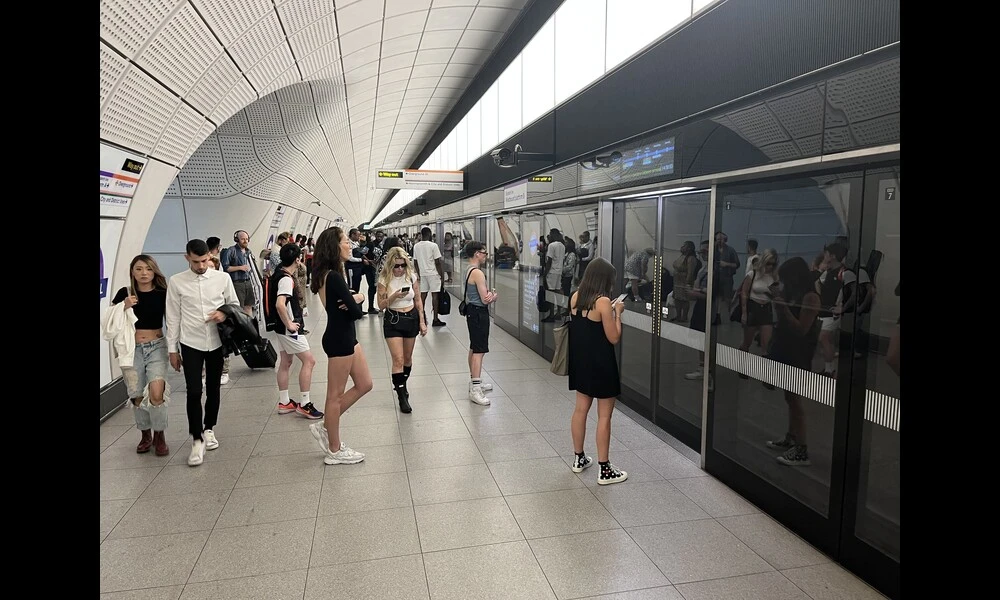 20230624 1430 Elizabeth tube line @ Whitechapel | David Wilson on Flickr
20230624 1430 Elizabeth tube line @ Whitechapel | David Wilson on FlickrNew research has introduced a novel metric for assessing the temporal concentration of travel demand in urban transportation networks. The study, which focused on the London Underground (LU) network, found that stations located in areas with low residential, retail, and employment density experienced the most pronounced temporal concentration of travel demand. On the other hand, stations servicing high-density employment zones, particularly around the City of London, had a greater temporal concentration of travel demand compared to those catering to commercial and residential districts in West London.
The study highlights the importance of understanding and quantifying the concentration of travel demand in urban transportation networks. By doing so, policymakers and transportation planners can optimize resource allocation and improve planning efficiency. The research findings provide insights for enhancing public transport operations and optimizing workforce distribution.
The study utilized granular data from smart travel cards, which capture the location and time of entries and exits into the transportation network. Researchers used a methodological framework based on Random Forests and K-Means clustering to identify attributes of the transport network's locations that contribute to varying levels of temporal concentration of travel demand.
The research findings have broader implications for urban planning and policy decisions. By quantifying the temporal concentration of travel demand, policymakers can make informed decisions about public transport operations and interventions aimed at altering the urban dynamics of specific areas. The goal is to spread travel demand more evenly over space and time, reducing congestion during peak hours and improving the overall efficiency and comfort of urban transportation systems.
This study provides valuable insights into the complex dynamics of travel demand in urban areas. By understanding the factors that contribute to temporal concentration, policymakers can work towards creating more efficient and sustainable transportation systems that meet the needs of growing urban populations. The research lays the groundwork for further exploration of the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of travel demand and its implications for urban mobility.