New Retinal Scan AI Helps Find Disease Indicators
Published on Tue Feb 25 2025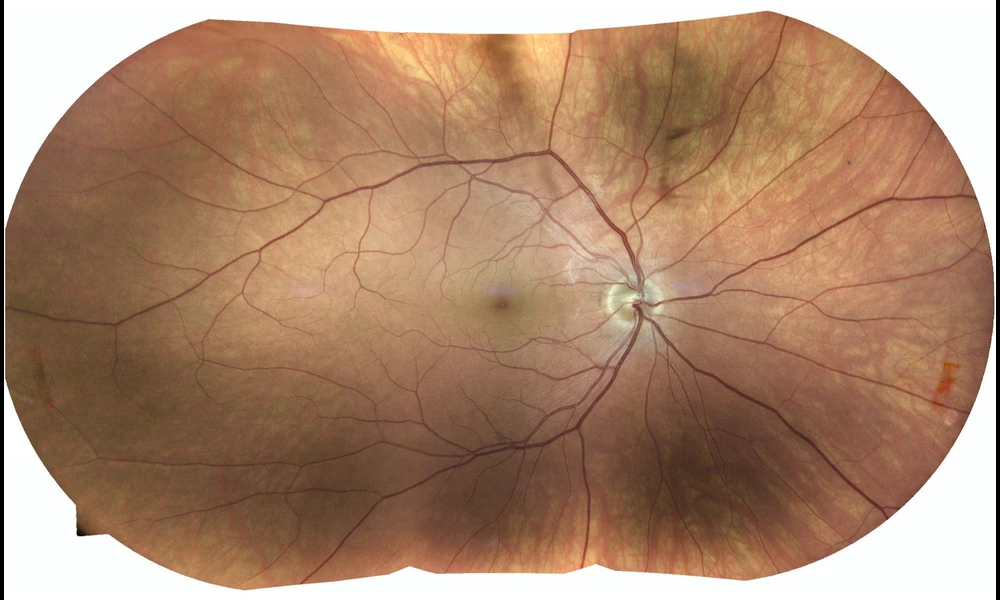 Look into my eyes | Steve Jurvetson on Flickr
Look into my eyes | Steve Jurvetson on FlickrFor most people, our eyes are the window through which we see the world; however, this metaphorical window can also be used in the other direction, offering unparalleled views of the central nervous and circulatory systems without invasive procedures. In a recent preprint paper, researchers in the United Kingdom showcase a method that effectively identifies and segments retinal vessels to provide crucial indicators of diseases even beyond eye health, including Parkinson's disease, hypertension, multiple sclerosis, and dementia, etc. potentially before the patient has symptoms. They accomplished this by creating a lightweight neural network that could one day be embedded in medical equipment.
The innovative approach revolves around a region-guided attention network built to operate efficiently even on devices with limited computational power. This is achieved by integrating depth-wise separable convolutions, reducing the network's parameter count without sacrificing accuracy. Such intricacies ensure the model is both robust and resource-efficient, providing detailed segmentation with improved accuracy compared to existing techniques. This could pave the way for broader applications in portable diagnostic tools, potentially enhancing access to early medical interventions.
One of the notable triumphs of this network is its employment of an attention mechanism called Inverse Addition Attention (IAA) blocks. These blocks hone in on the foreground regions, markedly improving the segmentation's focus on the actual vessels, ensuring the delicate and intricate structures of the retina are accurately captured. This aids in overcoming common imaging challenges like low contrast and imbalanced intensity that often mar the accuracy of retinal imaging.
Moreover, researchers harnessed the power of weighted Dice loss during network training, a strategic choice that mitigates the class imbalance often seen in medical image data. This ensures that false positives and false negatives are equally penalized, leading to more precise boundary delineation of the segmented images, thus enhancing the overall diagnostic ability of the retinal scans.
Extensive experimentation on widely recognized datasets, including DRIVE, CHASE_DB1, and STARE, reported superior performance across metrics such as recall, precision, and accuracy. The results not only confirm the model's efficacy but also underscore its potential to replace or supplement existing diagnostic practices with more efficient, scalable solutions.
This advancement represents a significant step in the field of medical imaging, showcasing a fusion of sophisticated algorithmic design with practical applicability. It holds promise not only in clinical settings but also for integration into consumer health devices, providing a panoramic window into systemic health via the eyes – simplifying healthcare accessibility and potentially redefining early disease detection paradigms.
As retinal imaging continues to be an invaluable tool in modern medicine, innovations like the Region Guided Attention Network solidify the path towards a future where quick, accurate, and non-invasive disease diagnostics become the norm. This research invites further exploration and adaptation within the medical community, heralding a new era of proactive healthcare management.