Martial Arts Training Boosts Vigilance and Flexibility in Adults
Published on Tue May 30 2023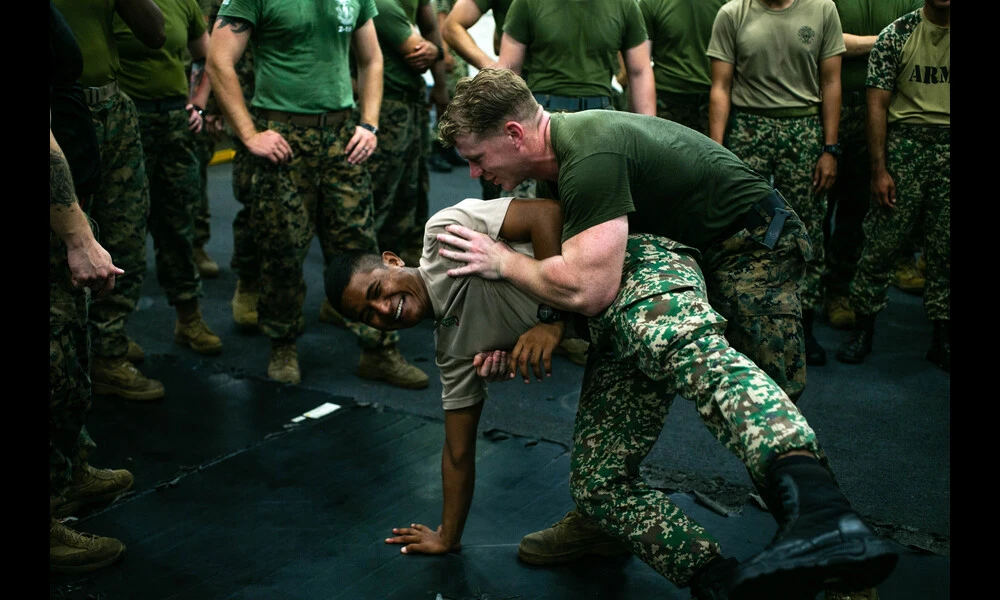 Exercise Tiger Strike 2019 | United States Embassy Kuala Lumpur on flickr
Exercise Tiger Strike 2019 | United States Embassy Kuala Lumpur on flickr
New research suggests that practicing martial arts can have a positive impact on both vigilance and cognitive flexibility. The study, titled "Vigilance & Cognitive Flexibility: The Effect of Martial Arts Experience on Task Switching," aimed to investigate the effects of martial arts training on these cognitive functions in typical adults.
Previous research has indicated that exercise and meditation can improve executive functions, such as cognitive flexibility, in adults. Martial arts, which combines physical exercise with intense concentration similar to meditation, was the focus of this study. The researchers recruited adult martial artists with at least two years of experience and compared their performance to a control group with no martial arts experience.
During the study, participants had to respond to either the shape or color of a figure in pure and mixed blocks. This allowed the researchers to measure mixing costs, which reflect sustained vigilance, and switching costs, which assess cognitive flexibility. The results showed that martial artists did not differ from the control group in the pure block. However, they displayed improved performance in the mixed block, indicating an improvement in mixing costs.
The findings are significant because vigilance and cognitive flexibility play crucial roles in our daily lives. Cognitive flexibility enables us to adapt our behaviors and choose the most effective responses, while vigilance allows us to detect stimuli and respond appropriately. Enhancing these functions can be valuable in developing interventions for individuals experiencing cognitive decline or dysfunction.
The difference in mixing costs associated with martial arts practice suggests that martial artists are able to maintain sustained vigilance at a similar level to non-martial artists in the pure block. However, they show improved performance in the mixed block, indicating enhanced vigilance. Interestingly, there was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of switch costs, which measure cognitive flexibility during task switching.
Overall, this study provides further evidence of the positive impact of martial arts training on cognitive functions. The findings suggest that martial arts practice can improve vigilance and potentially enhance cognitive flexibility in adults. This knowledge can be particularly beneficial in developing interventions to support cognitive health and function in individuals of all ages.